Image 1: Traditional off-the-shelf FDM 3D printer
Three-dimensional, or 3D printing, is one of the most beneficial technological advancements from the last few decades. It uses 3D models created in a computer to manufacture complex designs. Machines lay thin layers of a pre-selected material to create the design physically.
3D printing is also known as the additive manufacturing process. You can construct incredibly complex designs which may not be possible using traditional methods. Many industries are applying 3D printing solutions to their problems.
In this post, we will take a closer look at 3D printing and its applications in some of the major industries.
Materials Used
There are numerous materials used for this type of manufacturing based on specific product requirements. Metals, polymers, resins, and filaments are the most commonly used raw materials. The precise materials and their composition vary in each product.
Industrial Applications of 3D Printing
Many industries are using 3D printing extensively to improve their products. Some produce prototypes with this novel manufacturing process, while others manufacture parts used in their current products.
The potential applications of this technology are endless. However, due to cost and some other constraints, its usage is still limited. Let’s learn more about these industrial applications and how it is making a difference.
1. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry employs the most modern techniques in its product design to achieve maximum benefit. The main aim is to reduce fuel consumption and increase the speed of aircraft. 3D printing is a crucial part of some of the industrial processes. The 3D printed parts generally require less volume as well.
Example from the Industry
Ariane 6 is an underdevelopment rocket launching system developed for European Space Agency (ESA) by Airbus Group and Safran. One of the critical components for the launch is an injector head, as it’s a fundamental element in the propulsion module, which forces the fuel mixture into the combustion chamber.
Traditionally, there are dozens to hundreds of small parts that are put together. 3D printing helps create the device in a single piece with a nickel-based alloy. The additive manufacturing technique reduces three months of production time to 35 hours and lowers the cost by 50%.
2. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has similar aims to aerospace. They want their vehicles to be fuel-efficient. Some also want to add aerodynamics to make them faster, even by mere fractions of a second. They apply 3D printing solutions to counter a number of issues.
– Customization
Customization of parts for the interior as well as the exterior of the vehicle is a common practice. In most cases, a 3D printed material is far easier to produce and cost-efficient than traditional methods. Professional drivers often require customizations to their vehicles to get the maximum benefit from their cars on the track.
– Design Flexibility
Design flexibility is critical for research and development. With faster production of parts, 3D printing allows car manufacturers to experiment more with their components. Such experimentation leads to more efficient designs in vehicles.
– Spare Parts
Damage to car parts throughout a vehicle’s life is pretty standard. Replacing the damaged parts with new ones is also a common practice. 3D printing technology also helps in making higher-quality spare parts for vehicles. BMW is the first automaker mass-producing spare parts with the help of technology.
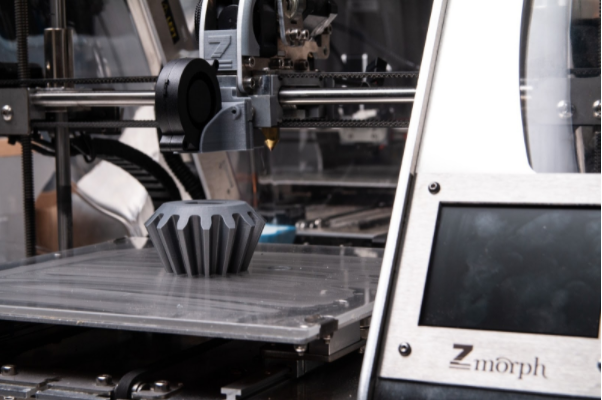

Image 2: An FDM 3D printer manufacturing a bevel gear that can be used as an end-use-product or for testing purposes
Example from the Industry
German Automaker Porsche uses 3D printing technology in seats for its vehicles, offering soft, medium, and stiff back and headrests. The motorsports industry frequently uses this technology to provide drivers with every bit of advantage. One can expect greater customization for comfort in these vehicles soon.
3. Medical and Dental Devices
The world of medicine and technology has been working together for ages to improve the quality of human life. 3D printing applications have played an essential part in this endeavor. From dental implants to better prosthetics to the production of artificial living tissue, 3D printing is making the world a better place.
Example from the Industry
Lima Corporate is an Italian company that produces 3D-printed orthopedic devices. They mainly make hip and knee joint replacements, spinal implants, and cranial reconstruction implants. They’re able to mimic these joints better due to the technology and offer better results.
Over half a million of these orthopedic devices were in use by 2019. The company expects the number will be over four million in the next few years.

Image 3: A print farm of Ultimaker 3D printers manufacturing arm casts for patients.
4. Consumer Products
There is a never-ending list of improvements 3D printing has introduced into consumer products. From shoes to razors, and from potato chips to bikes, there is some use of 3D printing. The purpose is obviously to improve their overall quality.
– Quicker Product Development
A company looks at multiple prototypes of a product before approving the best one. The process takes time and effort. However, with 3D printing, the time taken for the prototypes to be designed and produced is significantly lowered.
3D printing can make minor adjustments to the existing designs. With some tweaking, you can manufacture the right product. With faster product development, it takes less time to take the product to the end-user.
– Mass Customization Potential
Customization can be tricky for some products, especially using the traditional manufacturing processes. However, with 3D printing, customization at a mass level is very much possible. Instead of creating the same designs at a massive scale, 3D printing enables slight differences in structure aided by the computer.
Since it is easy for the printer to make that adjustment, you can customize products without compromising the production process. In the longer run, this can revolutionize the entire consumer goods industry by ordering customized merchandise the order of the day.
Example from the Industry
Racing bikes need to be light and provide every bit of advantage to the rider. Carbon fiber is the preferred raw material. California-based startup Arevo developed a single-piece carbon fiber frame traditionally assembled from multiple pieces for bike manufacturer Emery.
The innovation reduced the production time for the frame from 18 months to a few days and significantly lowered the production cost. It is truly a win-win situation.
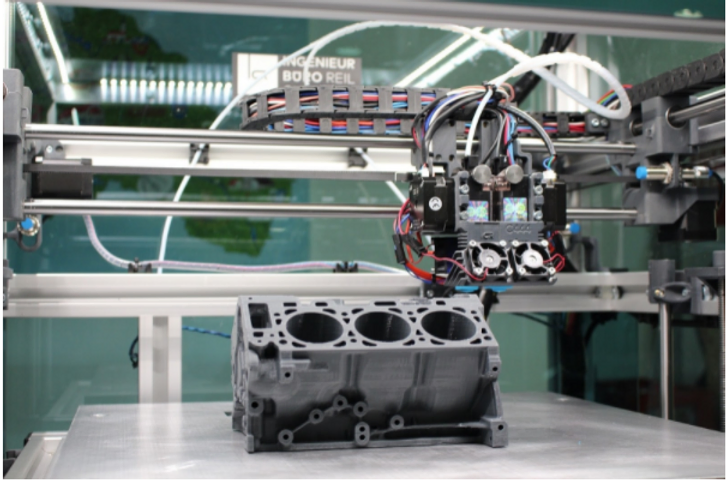
Image 4: An FDM 3D printer manufacturing a V6 engine block
The Conclusion
3D printing is a genuinely revolutionary manufacturing process and has limitless applications in various industries. In this post, we only discussed a few industries and how 3D printing makes them better.
This manufacturing process will eventually become a part of almost all industries. 3D printing helps people by improving the quality of their lives. Its contribution, for now, is limited. However, one can expect that this technology will be a major game-changer in the coming years.
The cost of printing and some raw materials is also a concern. The aerospace industry and automakers may be less worried about it for now due to the nature of their industries. However, for an ordinary person to truly benefit from 3D printing technology, it will need to become more cost-effective.