Simply upload your model, retrieve a quote in minutes and have your order delivered to your door free of charge

Simply order through a student email
500 x 500 x 500mm envelope
3 Days or 24 Hour Express
With a background in engineering, KAD3D is a team of experts! Request a FREE quote and get your model professionally printed FAST on our modern 3D printers in the material you require
Have an idea that you would like to see made into reality? Talk to us and see how we can make your ideas come true with 3D CAD modelling and 3D printing
Looking for some PLA or ABS filaments for your 3D printer? Check out our extensive range of colours and our exuberant variety of materials
Ready to purchase your own 3D printer? Let us take the worry away with our range of hand-selected, reputable 3D Printers within an affordable price for your needs.
Can’t get your 3D printer running? Alignment issues? Print failure? Read through our blog or join one of our many workshops to learn all the in’s and out’s of 3D Printing
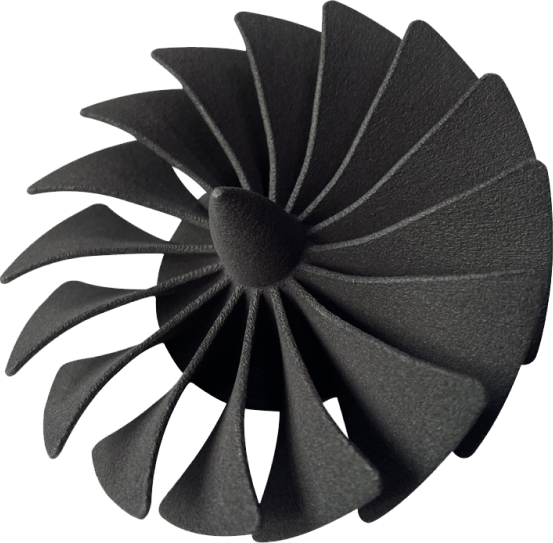
Considered the next manufacturing revolution, 3D Printing is the process of creating complex 3-dimensional objects from 2-dimensional models. See why thousands of industries are already adopting this revolutionary technology and why you should too
3D representation of your design to gain a greater understanding for yourself, investors or clients
Speed up the prototyping process by up to 87% by creating 3D models of your design
Wearable fashion in designs you’ve never seen before
Pizza, cakes, cookies, sugar, chocolate – all 3D printed and all edible
Create custom-made, exclusive jewellery and be unique
The ability to create custom fitting prosthetic limbs available to everybody
Easily fix anything around the home by printing your own spare parts
Shoes can be made to fit with just a click of a button
There are many great benefits to 3D Printing. Whether it be for personal use or for business, the advantages to this revolutionary technology are endless. Now is the best time to join the 3D Printing revolution.
Create innovative designs which would otherwise be impossible with traditional methods of manufacturing – jewellery, clothing, parts, architecture, engineering. The possibilities are endless
3D printing can significantly reduce costs in the design process by simply allowing you to hold your design in your very own own hands within mere hours
With a large range of environmentally friendly biodegradable materials, 3D printing will revolutionise the manufacturing industry while looking after the environment
For the same price as an iPhone, you too can have your very own 3D Printer and create anything you can imagine.








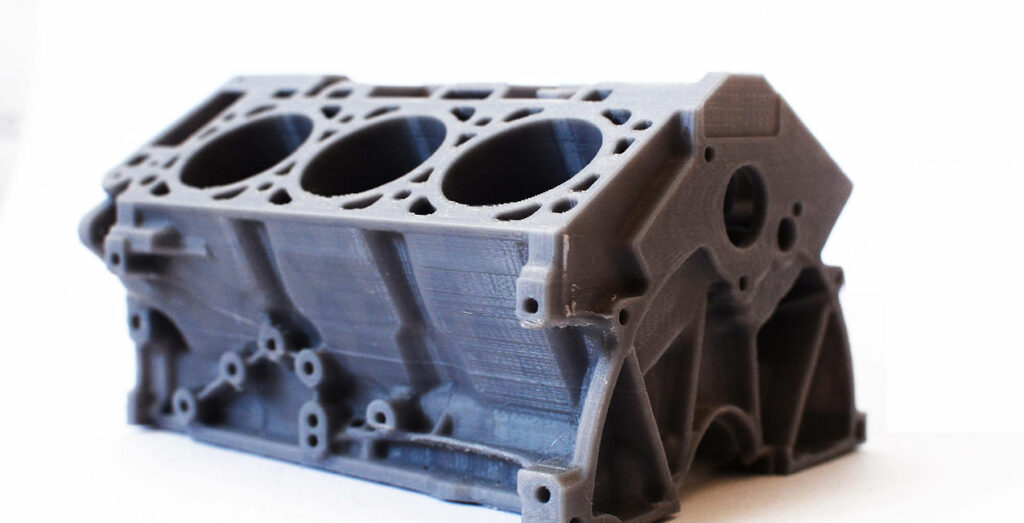
The process of additive-manufacturing has made it possible to create 3-dimensional objects, and what was once an object of science fiction has now become a reality. Not only has it become possible to custom create these objects and watch your ideas come to fruition in physical form, but it can also be done with relative affordability.
This process is initiated through the transmission of visual data digitally then the processing unit proceeds to lay thin layers of the specified material gradually and with precision until the object is correct. Experts and futurists have touted this technological breakthrough as the next industrial revolution. The possibilities in industry and manufacturing are now endless thanks to this development. It can potentially change our lives and the way that we can access various items and products. It can help to boost already existing mass production processes and also further enhance custom manufacturing as an industry.
At Kad 3D, we support the idea that 3D Printing is the future of industrial manufacturing in this country. Governments should be funding research and development into 3D Printing and it’s benefits. Moreover, the Education sector specifically should be heavily emphasizing the use of 3D Printers for students of all ages. Creators and entrepreneurs can also use this technology for model-making and prototyping; this should be supported by government grant incentives. The values that we pride ourselves on our quality assurance, speed of service and customer satisfaction guarantee; this is delivered by providing Sydney 3D Printing service Australia wide. You may be working on a project and require some custom plastic parts to be printed, or perhaps are looking to have something designed? Or maybe you are looking to prototype a model for production and sale? Kad 3D is your go-to 3D printing company for all of this and much more.
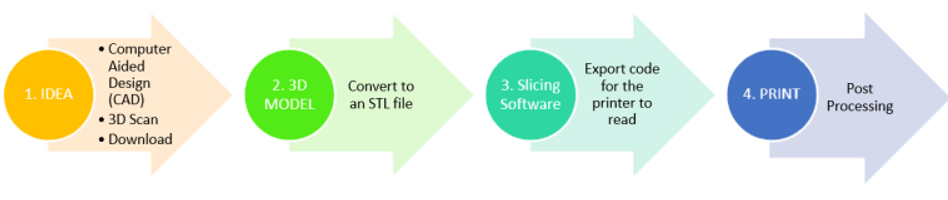
Conventional forms of manufacturing involve the need to cut into a slab of material in order to mold and shape the required item or object, this process is known as subtractive manufacturing. 3D Printing, on the other hand, is known as additive manufacturing. Material is built up gradually, layer upon layer in order to complete the production of the object. A computer-aided design in the case of 3D Printing is utilised and transmitted digitally, either through data cable or mass storage device, to the 3D printer. The printer then takes the image and proceeds to build layer by layer of the specified material in order to complete the object.
3D printing provides an opportunity for you to see your idea completely materialised in physical form. Traditionally, creating an item of this nature would require contracting a company in manufacturing, which would cost a lot of money because major manufacturers produce items in mass for large scale sale and distribution, as opposed to 3D printing where you can custom create an item to suit your needs in a fraction of the time and cost. The following are the most significant advantages to 3D Printing:
3D Printing is faster than traditional subtractive and injection-mold methods. Whether it be a test model or a prototype product, 3D Printing provides the flexibility and consistency for the benefit of clients and customers alike.
3D Printing eliminates the potential for poor craftsmanship and human error. Optimised design based on the specifications of the required object to be printed and based on the type of printer, helps to minimise the risk of a failed print and can help to reach a positive outcome
Conventional manufacturing is predominantly large scale operations, whereby heavy machinery is operated by highly skilled technicians, this process is costly taking into consideration the cost of labor and the cost of operating the machines. 3D printing on the other hand, significantly reduces the chain of command and over-heads; and often a single operator initiating a print command will suffice.
Due to the luxury of fast print and turn-around time, the opportunity to do extensive testing is afforded. You are able to conduct comprehensive testing in order to locate potential flaws and if necessary, make digital modifications to the CAD design file to initiate a re-print.
Conventional manufacturing is based around the idea of mass production for mass consumption, there is very little room for customisation. Whereas in the case of 3D Printing, the opportunity to create a fully customised and personalised object is afforded, the only limitation, in this case, is the creativity of the designer and the capacity of the chosen printer.
Rather than producing items on a large scale, which has been the case traditionally, and running the risk of a bad production line due to minor flaws; 3D Printing gives the benefit of producing on a small scale for testing before embarking on potential major production.
3D Printing provides a wide array of options with regards to the material that can be used to produce a physical object. Some of these include plastic, glass, metal, wood, paper, bio-material, ceramics, etc.
Conventional manufacturing processes involve the production of a lot of waste due to the subtractive approach, however 3D printing being an additive approach uses much less waste often only requiring the material needed to produce the object and in some cases minor support material.
Less human resources mean a reduction in risk of injury. Furthermore, eliminating the need to operate heavy machinery means less potential for short term and long term health issues.
Being a relatively new technology, 3D Printing provides the opportunity to learn, the same way that the introduction of personal computers to schools changed the way children learned in the early ’90s, introducing 3D Printers into schools and incorporating them as a learning tool in the curriculum can influence an entire generation. 3D design and printing teaches students how to create an abstract digital design and then watch it come to life reducing the need for physical craftsmanship. The trial and error process can also help students to understand optimisation methods and design techniques in dealing with complex prints; locating flaws and making necessary digital changes to understand why a print may have failed and rectify it. Moreover, 3D Printers are usually modular, this can also be a teaching mechanism, whereby changing, replacing and modifying internal printer parts can become part of the learning process.
Over the past decade or so different types of printing methods have been developed and utilised to enhance the 3D Printing process.
These methods have advantages and disadvantages based on their application; here are some of the major and most commonly used:
FDM is probably the most commonly used method and used in cheaper printers and also in some higher-end printers. This process works by constructing a model layer by layer, starting from the bottom and building vertically. This works by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament. One of the greatest strengths of this method is that it uses production-grade thermoplastics, which ensures a robust finished product due to sound chemical and thermal attributes.
This method works by using high powered laser to fuse tiny particles of raw material to form the required 3D object.
This method works by using a high-powered laser to harden liquid plastic and creat a 3D object. This is the oldest method of 3D printing and is still widely in use today.
This method is similar in concept to an inkjet printer. Where an inkjet printer jets drops of ink, the Jetting 3D printing method involves jetting droplets of photopolymer which will then solidify when it is exposed to Ultra Violet light. The layers of photopolymer are layered one on top of the other until the 3D model is complete.
Not dissimilar to Laser sintering, this method uses a high powered laser to fuse together small particles, in this case, those particles are in the form of powder metal. The printer spreads the powdered metal to form the shape of the required object while the laser fuses and binds the metal in place.
3D Printing can potentially provide a practical solution to a complex problem; a unique way to address a problem or create something specific that otherwise cannot be sourced. Here are some important factors to consider in purchasing a 3D printer:
Users can save a lot of money by creating almost everything from smartphone cases to paper towel holders, reducing household expenses while adding a personal customized touch to their home.
Users are able to choose and produce the items they want when they receive the item will depend on how soon they can initiate a print rather than having to wait for a product to arrive in the mail.
Rather than purchasing an item that is mass-produced, users are able to custom design and print an item to their liking and the only restriction is their own creativity and the specifications of the chosen printer.
3D printing can be a great teaching tool and a great learning tool. It can help children to understand art, design, and engineering in a fun and interactive way whereby they are able to see their own digital creations come to life in physical form.
This is a major consideration to make as 3D printing’s fundamental advantage is being able to create whilst producing the least possible waste. Most contemporary 3D Printers have a high energy rating, so in terms of energy consumption, it isn’t as demanding as almost all counter-part manufacturing equipment.
We at Kad 3D provide a competitive 3D Printing service domestically. And you can get started with us today easily by accessing our user-friendly website, uploading your design file and taking advantage of our free quoting service. We pride ourselves on being able to offer the shortest turn-around time for a print job in the industry domestically whilst still maintaining high-quality prints. If your order is urgent and needs it to be fast-tracked, select our priority printing option and have it done in a day.
Our 3D Printing Sydney service is also able to cater to potential clients in other states including; Victoria, Queensland, Western Australia and South Australia. If you have an idea to design or print something, contact us and watch your idea come to life.
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene plastic is used in common products such as Lego.
An abbreviation for the term Computer-Aided Design used to describe a 3D model developed using computer modeling software. Examples are Solidworks, Google SketchUp, Autodesk Rhino, etc.
In 3D modelling, the technique of “pulling” the face of a 2D shape upwards or outwards, so that it becomes a 3D prism.
Fused Deposition Modelling printers are the most common type of 3D printer in schools, due to their relative affordability. FDM printers melt plastic filament and lay the melted plastic row-by-row, layer-by-layer to build up an object.
The list of instructions for a 3D printer to print an object.
A digital 3D object before it is printed into a real object. The process of designing such an object on a computer or tablet is called modeling.
Polylactic acid plastic is a plant-based polyester. It is the most recommended 3D printing filament for schools due to showing much lower particle emissions compared to ABS plastic.
Stereolithography. A 3D printing method whereby resin is cured using a UV light layer by layer until an object is formed. This is usually done upside down using a tank full of liquid resin.
Selective Laser Sintering involves printers using a large bed of powder and a laser to solidify layers until a 3D model is formed in a bed of powder, typically nylon.
The process where 3D printing software analyses the geometry in a model and prepares a list of instructions for a 3D printer to print the object. The list of instructions is stored as a g-code. Most consumer 3D printers ship with proprietary software that incorporates slicing just before printing.
A computer file with the extension STL. Each STL file stores the 3D geometry for a model. It is by no means the only file format for storing 3D geometry, but it is very common in the 3D printing world.
In engineering, extra space between two parts (eg. a shaft in a hole) to allow for different kinds of movement.